
Sonia Adriaty – Industrial Park
Introduction
What if your factory could think on its own, adapt to challenges, and make smarter decisions— effortlessly? Welcome to the Fourth Industrial Revolution, or Industry 4.0 —a transformative era reshaping how we produce, connect, and innovate. Building on the digital advancements of the Third Industrial Revolution, Industry 4.0 integrates advanced technologies to bring unprecedented connectivity and intelligence to production processes.
Picture factory systems that communicate effortlessly, collect real-time data, and make automated decisions to optimize efficiency and reduce human error. This is the essence of Industry 4.0: not just a technological upgrade, but a fundamental rethinking of how we approach manufacturing.
In this new landscape, the ability to process vast amounts of data and make quick, informed decisions is key to tackling today’s complex business challenges. Manufacturers must embrace technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and automation to thrive. These innovations create dynamic systems that adapt to change, streamline operations, and accelerate innovation in products and processes.
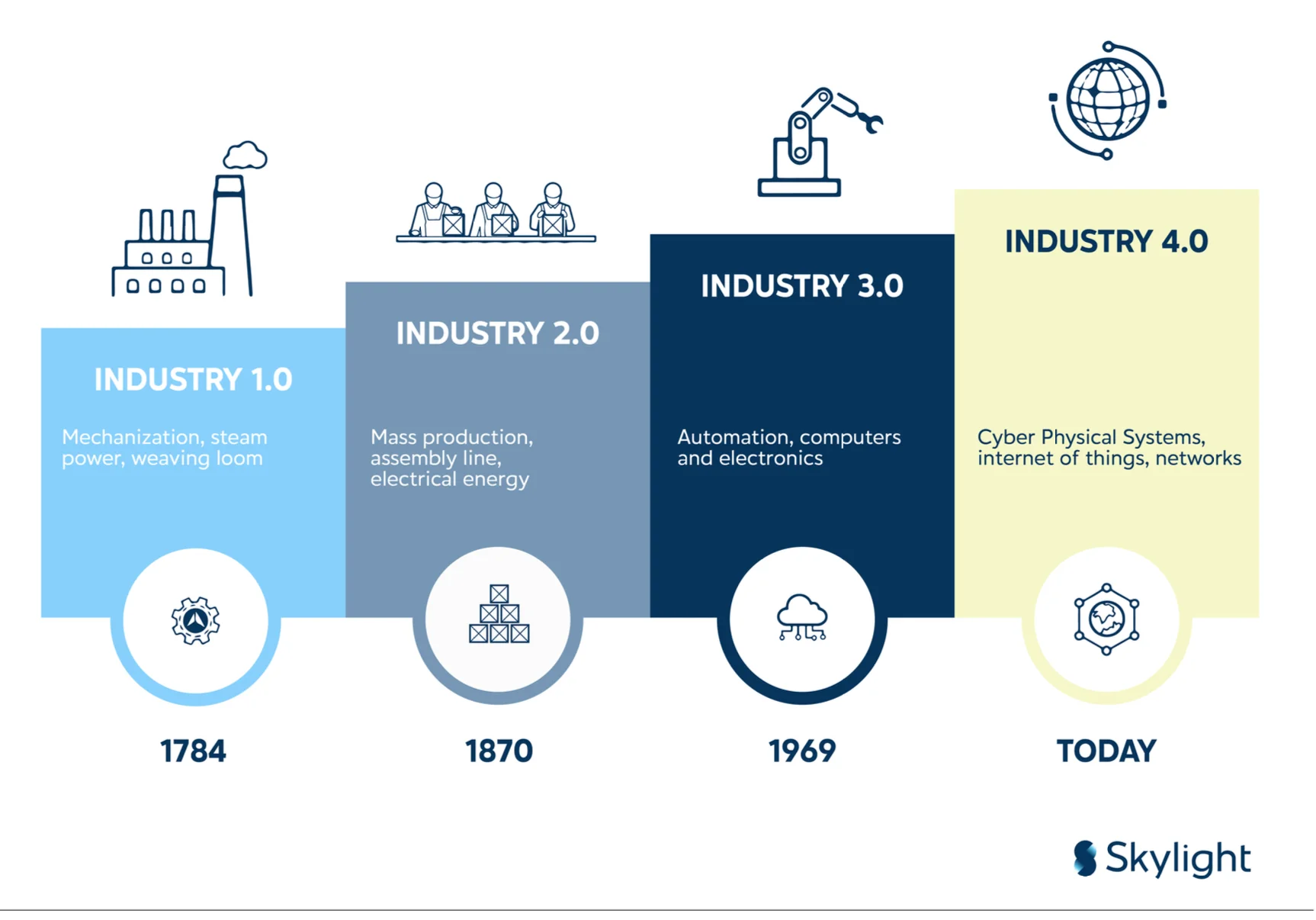
Industry 4.0 in Indonesia
It all began in 2011 when the German government launched an initiative at the Hannover Messe, the world’s largest industrial fair, aiming to modernize Germany’s manufacturing sector. The idea was to integrate cutting-edge digital technologies like IoT, cyber-physical systems, AI, and big data into production processes, helping Germany’s industrial giants stay competitive in the global market.
Over time, the concept spread beyond Germany’s borders, influencing industries across the world. The magic of Industry 4.0 lies in the way it connects factory systems, allowing them to communicate with each other and make decisions in real time. Instead of relying solely on human intervention, machines can now detect issues, alert operators, and even fix problems without halting production. This boosts efficiency, reduces costs, and minimizes human error.
Countries like China, Japan, and the United States quickly embraced the Industry 4.0 wave. China launched its “Made in China 2025” initiative, focusing on automation and smart manufacturing, while the U.S. developed programs like “Smart Manufacturing” and “Manufacturing USA,” promoting digital and automated technologies.
Indonesia, too, recognized the potential of Industry 4.0. In 2018, the government introduced the “Making Indonesia 4.0” initiative, aiming to modernize the country’s manufacturing sector by integrating technologies such as IoT, AI, big data, and robotics.
The “Making Indonesia 4.0” roadmap highlights five priority sectors poised for transformation and efficiency improvements through digital technologies: 1) Food and Beverages; 2) Textiles and Apparel; 3) Automotive; 4) Chemicals; 5) Electronics that are considered to have great potential to be transformed and improved in efficiency with digital technologies.
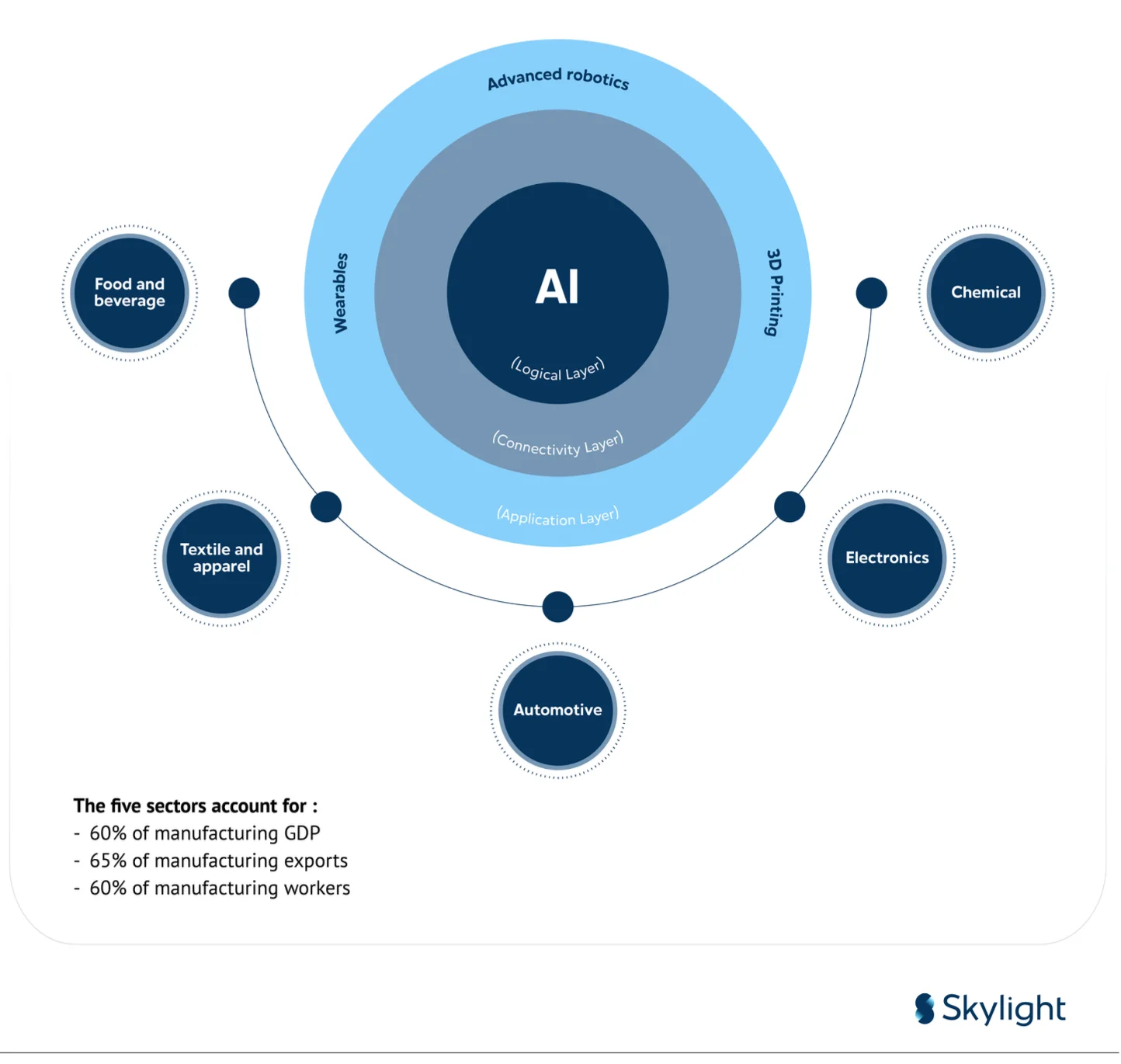
This focus on digitalization underscores the broader challenges faced by nearly all sectors of the manufacturing industry in Indonesia, from the availability of domestic raw materials to industrial policy issues. In response, the “Making Indonesia 4.0” initiative also includes 10 national priorities that are cross-sectoral, designed to accelerate the development of the manufacturing industry in Indonesia through targeted government interventions:

Lessons From the Ground
Major industries in Indonesia are already adopting advanced technologies in alignment to industry 4.0 to remain globally competitive:
1. Textiles and Apparel: Companies like PT Indorama Synthetics use IoT to track machine performance, improve maintenance, and reduce production downtime.
2. Food and Beverages: Nestlé Indonesia has embraced robotics for packaging and big data to analyze product demand, optimizing both production and distribution.
3. Electronics: PT Panasonic Manufacturing Indonesia employs collaborative robots (cobots) to boost efficiency in assembling components and uses data analytics to manage quality control and supply chains.
4. Energy and Mining: Pertamina utilizes IoT and big data for predictive maintenance in its oil drilling operations, which helps increase safety and efficiency.
5. Chemicals: PT Chandra Asri Petrochemical applies IoT to monitor critical factors like temperature during production, ensuring safety and product consistency.
Achievements and Future Challenges
According to Government Regulation (PP) No. 14 of 2015 on the National Master Plan for Industrial Development (RIPIN) for the years 2015–2035, the industrial services sector plays a crucial supporting role in Indonesia’s industrial development. It’s not just a background player—it’s a driving force that enables effective, efficient, and comprehensive industrial growth. By supporting manufacturing and other sectors, it helps boost the national GDP and contributes to the economic engine of the country.
Fast forward to the launch of Indonesia’s “Making Indonesia 4.0” roadmap, and the manufacturing sector continues to lead the charge. In fact, in the second quarter of 2024, Indonesia’s GDP growth hit an impressive 5.05%, outpacing giants like China, Russia, and Brazil. The non-oil and gas processing industry, in particular, was a standout contributor, accounting for 16.70% of the national GDP with a growth rate of 4.63%.
On the global stage, Indonesia’s Manufacturing Value Added (MVA) hit USD 255 billion in 2023, ranking 12th worldwide. This achievement places Indonesia ahead of ASEAN neighbors like Thailand and Vietnam, and even surpasses economic powerhouses such as the United States, Japan, Germany, South Korea, France, and the United Kingdom.
Minister of Industry Agus Gumiwang Kartasasmita highlights that this success is directly tied to the accelerated implementation of the “Making Indonesia 4.0” roadmap—a key part of Indonesia’s vision to become one of the world’s top 10 economies by 2030.
But, like any ambitious journey, there are hurdles. Industry 4.0 in Indonesia faces 10 key challenges, which Skylight has identified. Check out the image below for a closer look at these challenges and how they shape the future of Indonesian manufacturing:

Downstream and Industry 4.0
In the Draft of the 2025–2029 National Medium-Term Development Plan (RPJMN), the government targets an 8% economic growth, with the manufacturing sector contributing 21.9% to the GDP ratio.
The strategy being implemented focuses on creating new sources of growth on the production side that are evenly distributed across Indonesia. For example, in the industrial sector, there is the development of broad-based selected processing industries such as labor-intensive industries, basic chemicals, semiconductors, and the downstreaming of key mineral resources and natural resources (such as EV battery production and the circular economy). Additionally, the development of new growth centers such as Industrial Parks and Special Economic Zones, along with their supporting infrastructure, is also emphasized. Downstreaming is plays a crucial role to achieving an 8% economic growths, as it helps reduce dependency on raw material exports, creates new job opportunities, and has a positive impact on increasing community income.
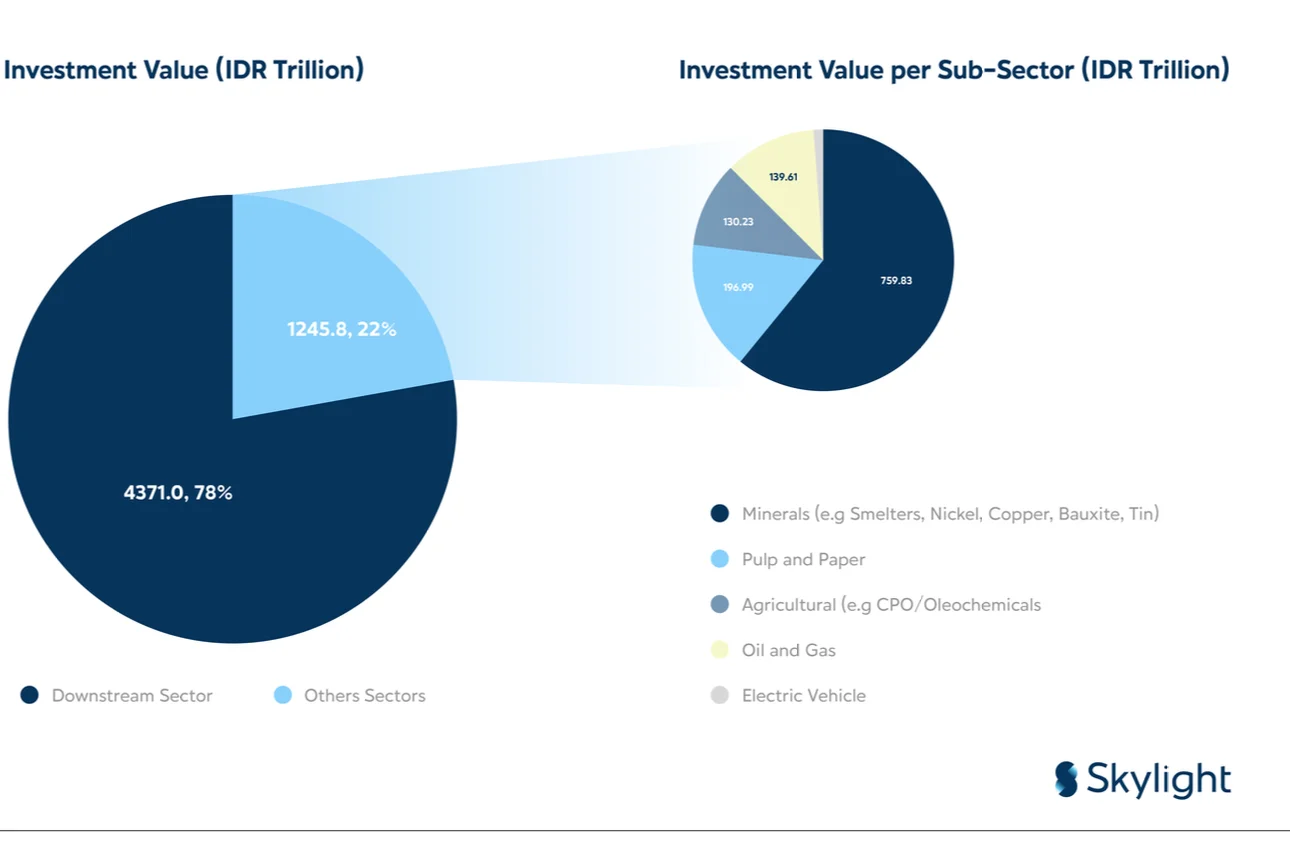
The Ministry of Investment and Downstreaming/BKPM recorded since the acceleration of downstreaming in 2020, marked by the nickel export ban policy, until September 2024, the total investment in the downstream sector reached Rp 1,245.8 trillion, accounting for 22.18% of the total current realized investment. This investment is distributed across various sectors such as minerals (Rp. 759.83 trillion); downstream forestry (Rp. 196.99 trillion); agriculture (Rp 130.23 trillion); oil and gas with Petrochemicals (Rp 139.61 trillion); electric vehicle ecosystem (Rp 19.14 trillion).
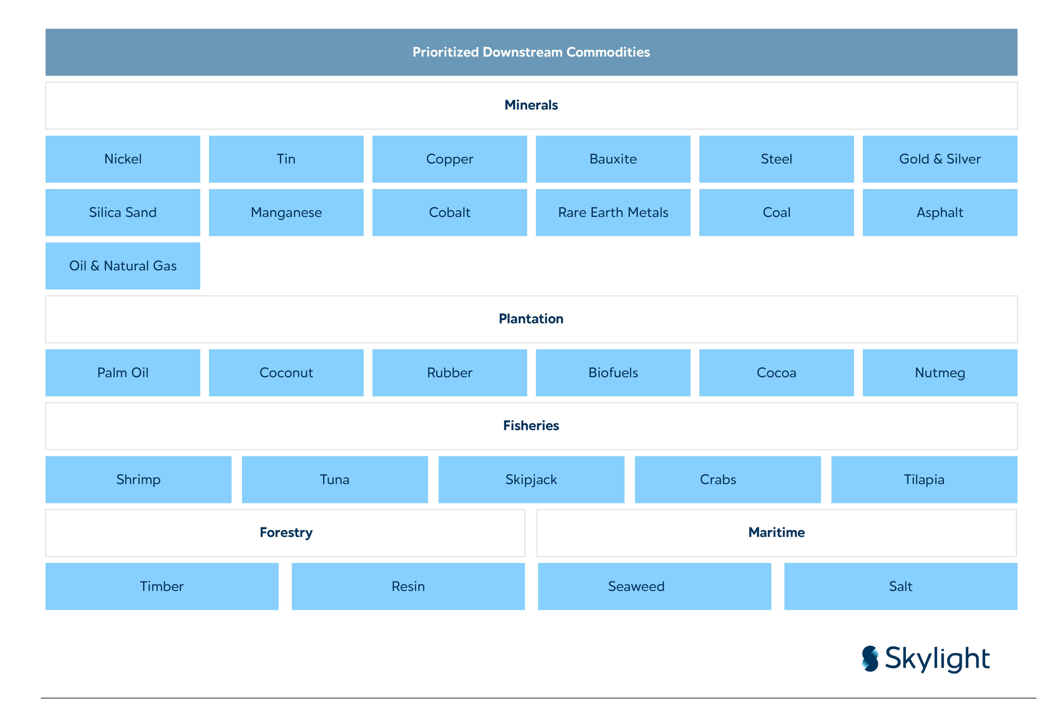
Previously, the Downstreaming Roadmap 2022-2023 served as a reference for creating added value from natural resource commodities. Currently, the government is refining its approach to key commodities. There are 28 prioritized downstream commodities in the current roadmap:
Unique Opportunities
In line with government policies encouraging industrial downstreaming, Indonesia is increasingly focused on optimizing the potential of the manufacturing sector by processing and enhancing the added value of natural resources. This downstreaming policy presents significant opportunities for certain sectors, such as minerals, agriculture, chemicals, energy, and electric vehicles, which are currently prioritized for development.
On the other hand, Industry 4.0 serves as a catalyst that can support downstreaming policies by providing high-tech solutions to increase productivity, efficiency, and competitiveness of the products being produced. The integration of Industry 4.0 with downstreaming policies holds great potential to boost Indonesia’s competitiveness in the global market, by creating higher-value-added products that are more competitive, efficient, and sustainable. Businesses that can quickly adapt to these changes will benefit greatly, in terms of cost efficiency, product innovation, and access to international markets.
Source:
1. Skylight Analytics Hub
2. Kementerian Perindustrian Indonesia. (2018). Making Indonesia 4.0.
3. McKinsey & Company. (2020). Indonesia’s Digital Transformation: Opportunities and Challenges.
4. Deloitte. (2019). The Future of Manufacturing in Indonesia.
5. PwC Indonesia. (2020). The Road to Industry 4.0: Insights for Indonesia.
6. World Economic Forum. (2019). The Fourth Industrial Revolution: Challenges and Opportunities.
7. OECD. (2020). Digitalization and Industry 4.0 in Indonesia: Issues and Solutions.
8. UNDP. (2019). Inclusive Growth and Digital Transformation in Indonesia.
9. Ringkasan Rancangan Awal RPJMN 2025-2029, Kementerian PPN/Bappenas, 2024 https://rpjmn.bappenas.go.id/dokumen)
10. Bisnis Indonesia. (14 November 2024). Hilirisasi Menuju Indonesia Emas.
11. Kumparan.com. (https://kumparan.com/kumparanbisnis/menperin-kinerja-sektor-manufakt ur-turut-dipacu-penerapan-making-indonesia-4-0-23fH6WPhuy7/full)
